MaB (EN)
Man and the Biosphere is an Intergovernmental Scientific Programme launched in 1971 by UNESCO. The main objective of the programme is to establish proper and sustainable relations between people and biosphere with valuable natural resources. To achieve this aim The World Network of Biosphere Reserves was created.
The World Network of Biosphere Reserves currently includes 783 sites in 134 countries all over the world, 22 of them are trans-boundary sites. Biosphere reserves are being established by the International Coordinating Council (ICC) of the MAB programme on member country request. Biosphere reserves remain under the sovereign jurisdiction of the states where they are located. Their main task is to gain sustainable balance between protection of biodiversity, support human resources development and preserve cultural values. The status of a Biosphere Reserve does not mean any extra formal protective regime it only serves the promotion of “areas for which characteristic is sustainable relation between people and biosphere”.
Biosphere reserves have three fundamental functions:
- Conservation: protecting landscapes and ecosystems, genetic and species variation.
- Development: fostering economic and human development that is environmentally and socially sustainable and culturally appropriate.
- Logistic support: facilitating demonstration projects, environmental education and sustainable development education and training, research and monitoring. While education, research, monitoring and capacity enhancement are seen as components of the logistic or knowledge-generation function of biosphere reserves, they are also integral to the conservation and development functions.
Biosphere reserves are usually being protected by division into core zone (strictly protected areas such as national parks, reserves and similar), buffer zone and transitional zone. World Network of Biosphere Reserves UNESCO currently includes eleven sites in Poland, among them five are trans-boundary.
In March 2016 at the 4th World Congress of Biosphere Reserves the Action Plan for the Man and Biosphere Programme and World Network of Biosphere Reserves for years 2016-2025, called Lima Action Plan was adopted. The plan was approved at the 28th session of the Man and the Biosphere Programme International Coordinating Council (MAB-ICC). Lima Declaration was also adopted.
Lima Action Plan (2016-2025) contains a set of actions to guide UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme and the World Network of Biosphere Reserves. It is aimed at ensuring implementation of the new Strategy adopted in 2015 by UNESCO’s General Conference. This Strategy as a continuation of Seville Strategy (1995) and Madrid Strategy (2008), extends range of actions regarding climate changes, education about sustainable development and cooperation at a local level.
Tatra Transboundary Biosphere Reserve
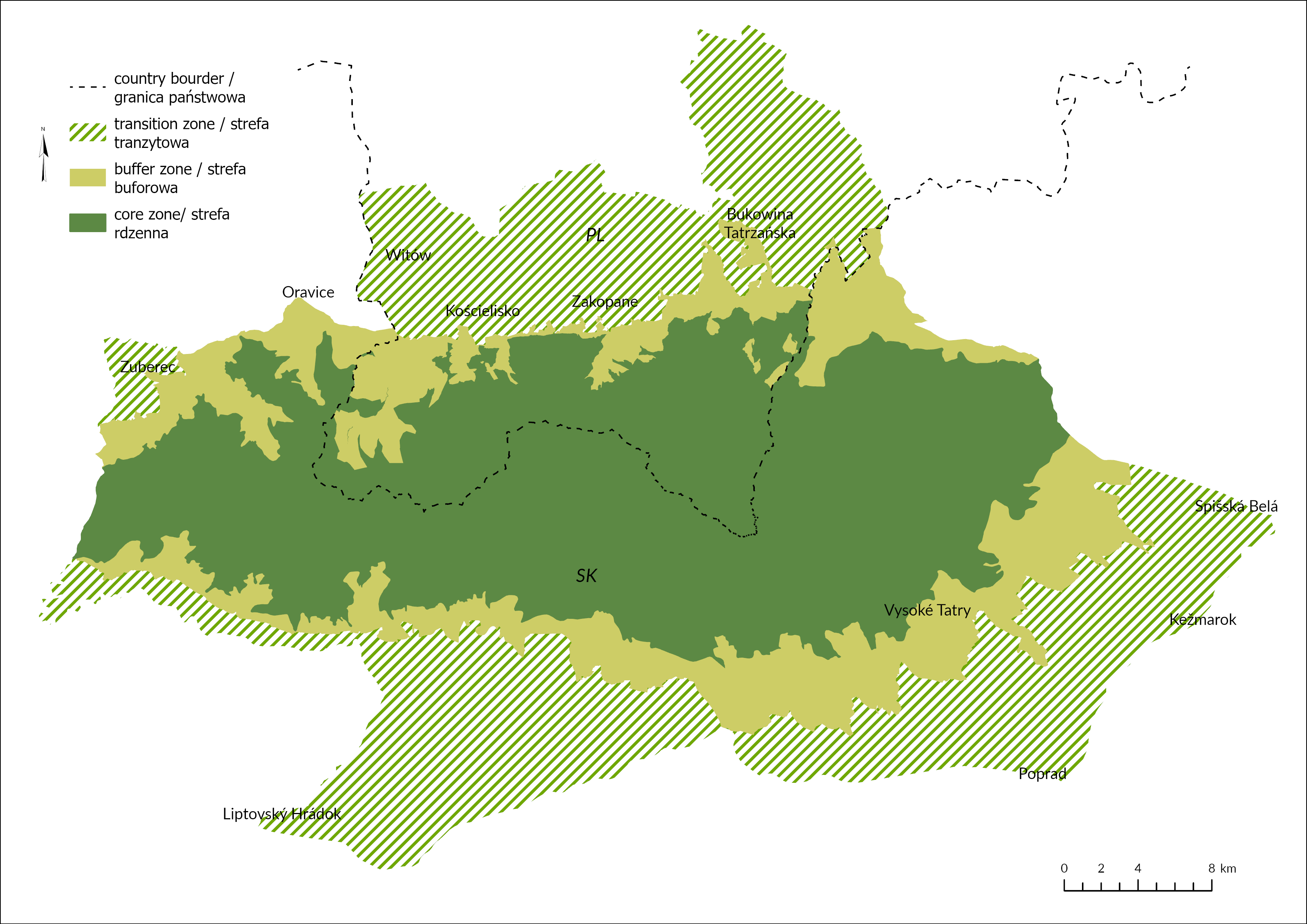
Tatra Transboundary Biosphere Reserve (TTBR) was created in 1992. Polish part of the reserve until recently was totally located within the borders of the national park. In 2019, the boundaries of the reserve were extended to include communes neighboring the park (Kościelisko, Zakopane, Poronin and Bukowina Tatrzańska). In the Slovak part biosphere reserve is located in the area of Sprava TANAP and Statne Lesy TANAP together with large area of national park buffer zone in the south and east. The total area of TTBR is 154 755 ha and it is divided into three zones: core, buffer and transitional.
The main function of the core zone is the protection of natural processes in the environment and minimizing human intervention in the ecosystems. The main function of the buffer zone is to enhance the protection and restore the original state of the environment. The transition area is located in the buffer zone periphery with relatively numerous and concentrated population and the main function is to coordinate the relationship between the protection and the production and traditional land use in sustainable way.
Tatra Transboundary Biosphere Reserve administrative bodies are: Tatra National Park for the polish side and Sprava TANAP for the Slovak side. Advisory function is performed by TTBR Steering Committee, which includes directors of national parks, representatives of local governments from municipalities located within or at the borders of the reserve, representatives of scientific world, non-governmental organizations as well as institutions and associations which conduct activities in the area of TTBR. Reserve’s functioning is regulated by the document: „Functioning of the Tatra Transboundary Biosphere Reserve – common action plan”.
The main strategic goals of the Tatra Transboundary Biosphere Reserve:
- Using Tatra TBR to conserve natural and cultural diversity, particularly in the Tatra TBR core area
- Using the Biosphere Reserve as a model of land management and approaches to sustainable development
- Using Tatra TBR for promotion, research, monitoring, education, training and building a regional identity.
Documents:
Lima Action Plan for UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme and its World Network of Biosphere Reserves (2016-2025): http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0024/002474/247418E.pdf